
by Terry Heick
Just how can you inform if a trainee really recognizes something?
They learn early on to play the game– tell the instructor and/or the test what they ‘wish to know,’ and even the most effective analysis leaves something on the table. (Actually, a huge part of the moment trainees just don’t recognize what they don’t understand.)
The idea of understanding is, obviously, at the heart of all learning, and solving it as a puzzle is just one of the 3 columns of official discovering settings and education.
1 What do they need to understand (criteria)?
2 What (and just how) do they presently comprehend (assessment)?
3 Exactly how can they best concerned comprehend what they presently do not (planning learning experiences and direction)?
Yet how do we know if they know it? And what is ‘it’?
Recognizing As’ It’
On the surface, there is difficulty with words ‘it.’ Seems vague. Bothersome. Uncertain. However everybody in some way knows what it is.
‘It’ is basically what is to be learned, and it can be a frightening point to both instructors and students. ‘It’ is every little thing, described with daunting terms like goal, target, proficiency, examination, exam, quality, fall short, and do well.
And in regards to web content, ‘it’ can be practically anything: a truth, an exploration, a habit, skill, or general idea, from mathematical theory to a clinical procedure, the value of a historical number to a writer’s function in a message.
So if a pupil gets it, beyond pure scholastic efficiency what might they have the ability to do? There are numerous existing taxonomies and characteristics, from Blossom’s to Understanding by Design’s 6 Elements of Understanding
The complying with activities are established as a straight taxonomy, from most fundamental to one of the most complicated. The best component regarding it is its simpleness: Most of these activities can be carried out merely in the class in minutes, and do not require complex preparation or a prolonged exam period.
By using a fast diagram, idea map, t-chart, discussion, picture, or short reaction in a journal, fast in person cooperation, on a leave slip, or by means of digital/social media, understanding can be assessed in minutes, helping to change screening and consternation with an environment of evaluation. It can be also be presented on a class web site or awaited the classroom to help guide self-directed understanding, with pupils inspecting themselves for understanding.
Just How This Comprehending Taxonomy Works
I’ll compose more about this quickly and place this into a much more graphic form quickly; both of these are critical in using it. (Update: I’m additionally producing a course for instructors to assist the, use it.) For now, I’ll say that it can be utilized to assist planning, evaluation, educational program design, and self-directed knowing. Or to create critical believing questions for any material area
The ‘Heick’ learning taxonomy is suggested to be basic, prepared as (primarily) isolated jobs that range in complexity from much less to a lot more. That stated, trainees needn’t demonstrate the ‘highest’ levels of understanding– that misreads. Any type of capacity to finish these tasks is a demonstration of understanding. The greater number of tasks the pupil can complete the better, however all ‘boxes inspected’ are evidence that the student ‘gets it.’
36 Assuming Approaches To Aid Trainees Duke It Out Intricacy
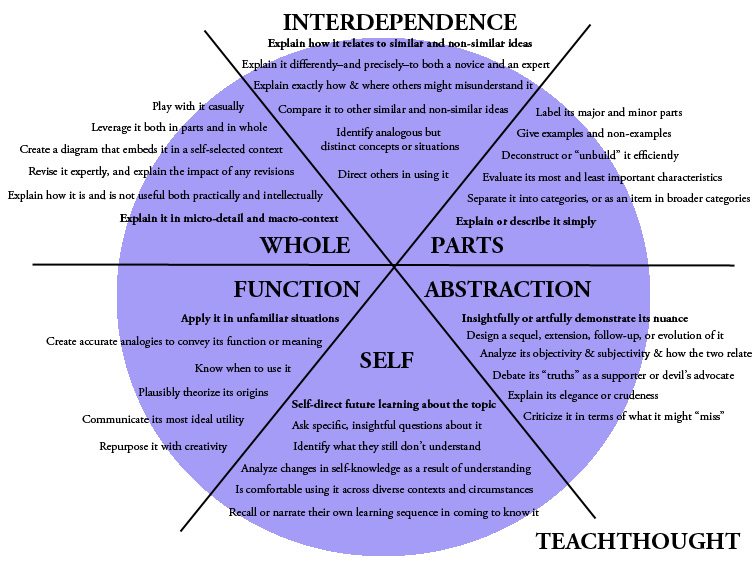
The Heick Learning Taxonomy
Domain name 1: The Components
- Describe or explain it merely
- Label its major and small parts
- Examine its most and least vital features
- Deconstruct or ‘unbuild’ it effectively
- Give instances and non-examples
- Different it right into categories, or as a thing in broader groups
Instance Topic
The War of independence
Test Prompts
Clarify the Revolutionary War in easy terms (e.g., an unpreventable rebellion that developed a brand-new country).
Determine the significant and minor ‘parts’ of the War of independence (e.g., economics and publicity, soldiers and tariffs).
Examine the Revolutionary War and recognize its the very least and essential qualities (e.g., caused and effects vs city names and minor altercations)
See likewise 20 Types Of Questions For Teaching Critical Believing
Domain 2: The Whole
- Clarify it in micro-detail and macro-context
- Produce a representation that embeds it in a self-selected context
- Discuss how it is and is not useful both almost and intellectually
- Have fun with it delicately
- Leverage it both partially and in whole
- Modify it adeptly, and discuss the effect of any alterations
Domain name 3: The Connection
- Discuss exactly how it connects to similar and non-similar concepts
- Straight others in operation it
- Discuss it in different ways– and exactly– to both a novice and a specialist
- Clarify specifically how and where others might misinterpret it
- Compare it to other similar and non-similar concepts
- Recognize comparable yet distinctive ideas, ideas, or scenarios
Domain 4: The Feature
- Use it in unknown situations
- Create exact analogies to communicate its feature or definition
- Evaluate the pleasant area of its energy
- Repurpose it with creativity
- Know when to utilize it
- Plausibly theorize its origins
Domain 5: The Abstraction
- Insightfully or artfully demonstrate its nuance
- Slam it in regards to what it might ‘miss’ or where it’s ‘deceitful’ or insufficient
- Discussion its ‘facts’ as a fan or devil’s supporter
- Clarify its beauty or indiscretion
- Assess its neutrality and subjectivity, and how both associate
- Style a follow up, extension, follow-up, or advancement of it
Domain 6: The Self
- Self-direct future finding out about the subject
- Ask details, informative questions regarding it
- Remember or tell their own understanding series or chronology (metacognition) in familiarizing it
- Is comfortable using it throughout varied contexts and situations
- Determine what they still don’t understand about it
- Evaluate modifications in self-knowledge as a result of understanding
Advanced Comprehending
Understanding by Design’s 6 facets of Recognizing, Bloom’s Taxonomy, and Marzano’s New Taxonomy were additionally referenced in the production of this taxonomy; a discovering taxonomy for recognizing